Genre Other. Page - 359

r VI and his son, Cesare Borgia, the Duke Valentino, and these characters fill a large space of "The Prince." Machiavelli never hesitates to cite the actions of the duke for the benefit of usurpers who wish to keep the states they have seized; he can, indeed, find no precepts to offer so good as the pattern of Cesare Borgia's conduct, insomuch that Cesare is acclaimed by some critics as the "hero" of "The Prince." Yet in "The Prince" the duke is in point of fact cited as a type of the man who rises on the fortune of others, and falls with them; who takes every course that might be expected from a prudent man but the course which will save him; who is prepared for all eventualities but the one which happens; and who, when all his abilities fail to carry him through, exclaims that it was not his fault, but an extraordinary and unforeseen fatality.
On the death of Pius III, in 1503, Machiavelli was sent to Rome to watch the election of his successor, and there he saw Cesare Borgia cheated into allowing th

, if not before. It is said thatDeucalion and Pyrrha created men by throwing stones over their headsbehind them:--
Inde genus durum sumus, experiensque laborum,
Et documenta damus qua simus origine nati.
Or, as Raleigh rhymes it in his sonorous way,--
"From thence our kind hard-hearted is, enduring pain and care,Approving that our bodies of a stony nature are."
So much for a blind obedience to a blundering oracle, throwing thestones over their heads behind them, and not seeing where they fell.
Most men, even in this comparatively free country, through mereignorance and mistake, are so occupied with the factitious cares andsuperfluously coarse labors of life that its finer fruits cannot beplucked by them. Their fingers, from excessive toil, are too clumsyand tremble too much for that. Actually, the laboring man has notleisure for a true integrity day by day; he cannot afford to sustainthe manliest relations to men; his labor would be depreciated in thema

angry. But his strength ebbed, his eyesglazed, and he knew nothing when the train was flagged and the twomen threw him into the baggage car.
The next he knew, he was dimly aware that his tongue was hurtingand that he was being jolted along in some kind of a conveyance.The hoarse shriek of a locomotive whistling a crossing told himwhere he was. He had travelled too often with the Judge not toknow the sensation of riding in a baggage car. He opened hiseyes, and into them came the unbridled anger of a kidnapped king.The man sprang for his throat, but Buck was too quick for him.His jaws closed on the hand, nor did they relax till his senseswere choked out of him once more.
"Yep, has fits," the man said, hiding his mangled hand from thebaggageman, who had been attracted by the sounds of struggle."I'm takin' 'm up for the boss to 'Frisco. A crack dog-doctorthere thinks that he can cure 'm."
Concerning that night's ride, the man spoke most eloquently forhimself, in a l
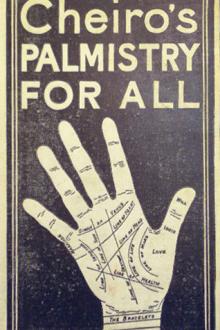
them to the readers of the American Edition of Palmistry for All.
CHEIRO.
LONDON.
INTRODUCTION
It was on July 21, 1894, that I had the honour of meeting Lord Kitchener and getting the autographed impression of his right hand, which I now publish for the first time as frontispiece to this volume. The day I had this interview, Lord Kitchener, or, as he was then, Major-General Kitchener, was at the War Office, and to take this impression had to use the paper on his table, and, strangely enough, the imprint of the War Office may be seen at the top of the second finger--in itself perhaps a premonition that he would one day be the controlling force of that great department.
Lord Kitchener was at that moment Sirdar of the Egyptian Army. He had returned to England to tender his resignation on account of some hostile criticism about "the Abbas affair," and so I took the opportunity of his being in England to ask him to allow me to add his hand to my collection, which ev

in politestudies.'CHAP. VII. Tsze-hsia said, 'If a man withdraws his mind fromthe love of beauty, and applies it as sincerely to the love of thevirtuous; if, in serving his parents, he can exert his utmost strength;
if, in serving his prince, he can devote his life; if, in his intercoursewith his friends, his words are sincere:-- although men say that hehas not learned, I will certainly say that he has.'CHAP. VIII. 1. The Master said, 'If the scholar be not grave, hewill not call forth any veneration, and his learning will not be solid.2. 'Hold faithfulness and sincerity as first principles.3. 'Have no friends not equal to yourself.4. 'When you have faults, do not fear to abandon them.'CHAP. IX. The philosopher Tsang said, 'Let there be a carefulattention to perform the funeral rites to parents, and let them befollowed when long gone with the ceremonies of sacrifice;-- thenthe virtue of the people will resume its proper excellence.'
CHAP. X. 1. Tsze-ch'in asked Tsze-kung,

"I'd like to," said Stella. "It would be a lot of fun."
"Come out Saturday evening and stay all night. He's home then."
"I will," said Stella. "Won't that be fine!"
"I believe you like him!" laughed Myrtle.
"I think he's awfully nice," said Stella, simply.
The second meeting happened on Saturday evening as arranged, when he came home from his odd day at his father's insurance office. Stella had come to supper. Eugene saw her through the open sitting room door, as he bounded upstairs to change his clothes, for he had a fire of youth which no sickness of stomach or weakness of lungs could overcome at this age. A thrill of anticipation ran over his body. He took especial pains with his toilet, adjusting a red tie to a nicety, and parting his hair carefully in the middle. He came down after a while, conscious that he had to say something smart, worthy of himself, or she would not see how attractive he was; and yet he was fearful as to the result. When he entered the sittin

ount. He thought so little about it that he overlooked any mention to the family. Much later he was questioned by my youngest brother Bishnu, who noticed the large deposit on a bank statement.
"Why be elated by material profit?" Father replied. "The one who pursues a goal of evenmindedness is neither jubilant with gain nor depressed by loss. He knows that man arrives penniless in this world, and departs without a single rupee."
[Illustration: MY FATHER, Bhagabati Charan Ghosh, A Disciple of Lahiri Mahasaya--see father1.jpg]
Early in their married life, my parents became disciples of a great master, Lahiri Mahasaya of Benares. This contact strengthened Father's naturally ascetical temperament. Mother made a remarkable admission to my eldest sister Roma: "Your father and myself live together as man and wife only once a year, for the purpose of having children."
Father first met Lahiri Mahasaya through Abinash Babu, {FN1-8} an employee in the Gorakhpur office of the Bengal-Nagpur Rail

fluence. The Republic of Plato is also the first treatise upon education, of which the writings of Milton and Locke, Rousseau, Jean Paul, and Goethe are the legitimate descendants. Like Dante or Bunyan, he has a revelation of another life; like Bacon, he is profoundly impressed with the unity of knowledge; in the early Church he exercised a real influence on theology, and at the Revival of Literature on politics. Even the fragments of his words when 'repeated at second-hand' (Symp.) have in all ages ravished the hearts of men, who have seen reflected in them their own higher nature. He is the father of idealism in philosophy, in politics, in literature. And many of the latest conceptions of modern thinkers and statesmen, such as the unity of knowledge, the reign of law, and the equality of the sexes, have been anticipated in a dream by him.
The argument of the Republic is the search after Justice, the nature of which is first hinted at by Cephalus, the just and blameless old man--then discussed on the

ITY.
Phantasmal mirth, folded away: muskperfumed.
AND NO MORE TURN ASIDE AND BROOD.
Folded away in the memory of nature with her toys. Memories beset his brooding brain. Her glass of water from the kitchen tap when she had approached the sacrament. A cored apple, filled with brown sugar, roasting for her at the hob on a dark autumn evening. Her shapely fingernails reddened by the blood of squashed lice from the children's shirts.
In a dream, silently, she had come to him, her wasted body within its loose graveclothes giving off an odour of wax and rosewood, her breath, bent over him with mute secret words, a faint odour of wetted ashes.
Her glazing eyes, staring out of death, to shake and bend my soul. On me alone. The ghostcandle to light her agony. Ghostly light on the tortured face. Her hoarse loud breath rattling in horror, while all prayed on their knees. Her eyes on me to strike me down. LILIATA RUTILANTIUM TE CONFESSORUM TURMA CIRCUMDET: IUBILANTIUM TE VIRGINUM CHORUS

things from the thoughts awakened in me by the speculations of St. Simonians; but it was made a living principle, pervading and animating the book, by my wife's promptings."[4] The part which is italicised is noticeable. Here, as elsewhere, Mill thinks out the matter by himself; the concrete form of the thoughts is suggested or prompted by the wife. Apart from this "general tone," Mill tells us that there was a specific contribution. "The chapter which has had a greater influence on opinion than all the rest, that on the Probable Future of the Labouring Classes, is entirely due to her. In the first draft of the book that chapter did not exist. She pointed out the need of such a chapter, and the extreme imperfection of the book without it; she was the cause of my writing it." From this it would appear that she gave Mill that tendency to Socialism which, while it lends a progressive spirit to his speculations on politics, at the same time does not manifestly accord with his earlier advocacy of peasant prop