Newton's laws by Sarah Joshway (ap literature book list TXT) 📖

- Author: Sarah Joshway
Book online «Newton's laws by Sarah Joshway (ap literature book list TXT) 📖». Author Sarah Joshway
Forces

( This picture is an example of contact force. The strength in which the boy is pushing the ball forward is tha force that allows the ball to fall to the ground. Because the boy is touchung the ball it is contact force)
-Strength or power exerted upon an object.
- push or pull
- Interaction between objects.
P.S. Force is a Vector magnitude and direction!
Two basic categories of Forces:
field forces
In physics a force field is a
vector field that describes a
non-contact force
acting on a particle at
various positions in space.
Examples: An everyday example is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. Materials that can be magnetized, which are also the ones that are strongly attracted to a magnet. Another example is the graviety that is applied constantly to your body as you go throughout your day. the feild force of graviety is pushing agaisnt you to keep you grounded.
Contact Forces:
In physics, a contact force
is a force that acts at the
point of contact between two objects
in contrast to body forces.
Contact forces are described by
Newton's laws of motion,
as with all other forces in dynamics.
Examples: Pushing a car up a hill or kicking a ball are some of the everyday examples where contact forces are at work. In the first case the force is continuously applied by the person on the car, while in the second case the force is delivered in a short impulse.
Unit of forces
-newton (n)
Newton's first law of motion
- sometimes referred to as the law of inertia.
Newton's first law of motion is often stated as
An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
There are two parts to this statement - one that predicts the behavior of stationary objects and the other that predicts the behavior of moving objects. The two parts are summarized in the following diagram.
Unblanced-There are two forces acting upon the book. One force - the Earth's gravitational pull - exerts a downward force. The other force - the push of the table on the book (sometimes referred to as a normal force) - pushes upward on the book.
Balanced-a person standing upon the ground. There are two forces acting upon the person. The force of gravity exerts a downward force. The floor of the floor exerts an upward force.
The behavior of all objects can be described by saying that objects tend to "keep on doing what they're doing" (unless acted upon by an unbalanced force).
If at rest, they will continue in this same state of rest.If in motion with an eastward velocity of 5 m/s, they will continue in this same state of motion. If in
The state of motion of an object is maintained as long as the object is not acted upon by an unbalanced force. All objects resist changes in their state of motion.
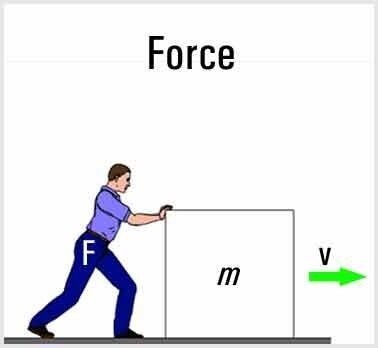
( The box that the man is pushig is most likely to stay at rest than an object in motion because the force in which the man is exerting on the object does not match the force needed to move an object that is in rest. However with more force applied it can be moved if a more unbalenced force is applied.)
Ever day example:
Have you ever experienced inertia (resisting changes in your state of motion) in an automobile while it is braking to a stop? The force of the road on the locked wheels provides the unbalanced force to change the car's state of motion, yet there is no unbalanced force to change your own state of motion. the unbalanced force is the same unbalanced force in Newton's first Law
Help:
to look a force again got to:
for help with Newtons fist law got to:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BlFGN2zlDYc
Newtons secound Law

(The acceleration of an object depends directly upon the net force acting upon the object, and inversely upon the mass of the object. As the force acting upon an object is increased, the acceleration of the object is increased. As the mass of an object is increased, the acceleration of the object is decreased. The child pulling the small rock has the proper net force and mass needed to move it. The children pulling the large rock is lease likely to move it because the the mass of the object has increased which will cause the acceleration of the object to decrease as stated in Newton's third Law.
- <<font;purple>font;24pt>The acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object.
-Newton's second law of motion is the behavior of objects for which all existing forces are not balanced. The second law states that the acceleration of an object is dependent upon two variables net force, and mass
- the net force
acting upon the object and the mass of the object. The acceleration of an object depends directly upon the net force acting upon the object, and inversely upon the mass of the object.The force acting upon an object is increased, the acceleration of the object is increased. As the mass of an object is increased, the acceleration of the object is decreased.
The acceleration is directly proportional to the net force
; the net force
equals mass times acceleration; the acceleration in the same direction as the net force; an acceleration is produced by a net force. The NET FORCE.
Newton's Third Law
Formally stated, Newton's third law is: To every action there is always opposed an equal reaction.
(The statement means that in every interaction, there is a pair of forces acting on the two interacting objects. The size of the forces on the first object equals the size of the force on the second object. The direction of the force on the first object is opposite to the direction of the force on the second object. Forces always come in pairs - equal and opposite action-reaction force pairs.)
A force is a push or a pull upon an object that results from its interaction with another object. Forces result from interactions!
-Whenever objects A and B interact with each other, they exert forces upon each other.
-When you sit in your chair, your body exerts a downward force on the chair and the chair exerts an upward force on your body. There are two forces resulting from this interaction - a force on the chair and a force on your body. These two forces are called action and reaction forces and are the subject of Newton's third law of motion.
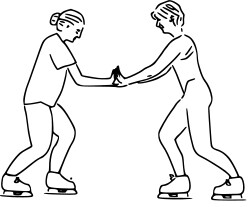
( in the picture above to people are two forces working agaisnt each other.If these forces countianue it will cause a reaction from the action of pushing agaisnt each other.)
Text: dont copy
Publication Date: 12-19-2011





Comments (0)